RAM, or Random Access Memory, is essentially a piece of hardware that stores your computer's short-term memory while the computer is running.
The difference between a RAM module and a data drive (whether HDD or SSD) is that RAM is volatile memory, meaning that data is completely erased when the power source is cut. On non-volatile types of memory, like a data drive, stored data is preserved in the absence of electricity.
Even though RAM is cleared every time you reboot, memory management has a significant impact on the performance of your system. We'll show you everything you need to know about RAM, how it works, and how you can possibly increase its efficiency.
The Various Types of RAM
DDR RAM, EDO, FPM, SDRAM, SIMM, DIMM... it can all be a bit confusing, especially if this is your first exposure to computer hardware.
These terms all describe different types of RAM modules that each differ in their physical properties. Generally, RAM modules fall into two types of categories:
- SIMM (Single In-line Memory Module)
- DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module)
SIMMs were first released in 1983 and are not commonly used today. With the advent of 64-bit processors, the 32-bit wide SIMMs had to be installed in pairs to remain compatible. Consequently, SIMMs have been replaced by 64-bit wide DIMMs, which can be installed individually.
EDO (Extended Data Out) and FPM (Fast Page Mode) are types of SIMM, while DDR (Dual Data Rate) and SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM) fall into the DIMM category. There's also a type called SO-DIMMs (Small Outline DIMMs) which are smaller in size and commonly found in laptops.

You might have noticed that DDR RAM comes in different versions, namely DDR, DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4. These are increasingly faster RAM modules that are not compatible with each other.
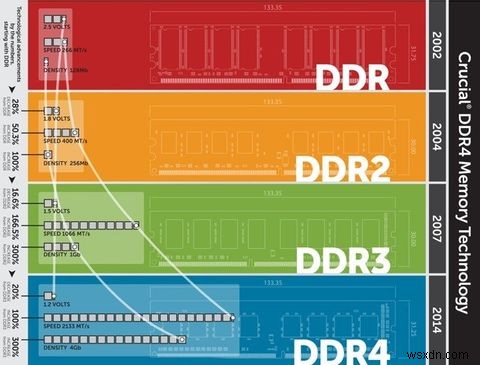
If this terminology fascinates you and you would like to know more about it, have a look at our Quick & Dirty Guide to RAM for fascinating facts about computer memory.
RAM Capacity, Frequency, and Latency
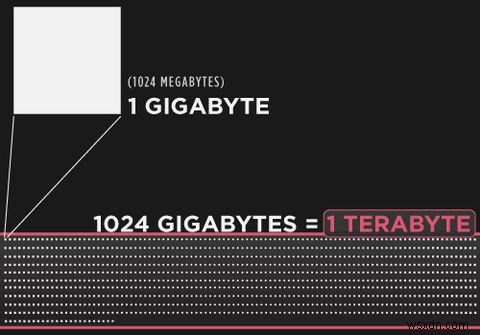
The storage size, or Capacity, of RAM modules is measured in megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes (MB, GB, and TB, respectively). For example, Windows 10 Professional 64-bit can support up to 2 TB of RAM.
On a 32-bit system, you can unlock up to 64 GB of RAM using a physical address extension (PAE) Patch. On the average computer, however, you're more likely to find between 1 and 4 GB of RAM installed, which is sufficient for most casual users.
The Frequency is measured in MHz and higher numbers potentially indicate faster access to the information stored in memory. This is a key factor if your graphics card shares your RAM. Latency describes the delay between a request and execution of the task, meaning lower numbers are better.
Together, Frequency and Latency affect the speed of your RAM.
A higher frequency, which makes RAM faster, can compensate for higher latency, which makes RAM slower. Generally speaking, however, you should prioritize capacity over frequency and latency. More is always better.
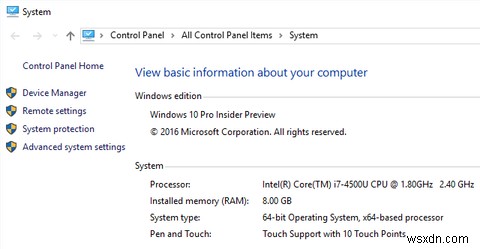
To see how much RAM is installed on your Windows computer, open File Explorer, right-click on This PC, and select Properties. This will open the System page in your Control Panel, which reveals the capacity of installed memory (RAM).
To find out the specs of your RAM, you need to use a tool like CPU-Z, which can analyze your system specs. This will also reveal whether your RAM runs as advertised by the manufacturer. For instructions on how to read the results of CPU-Z, please refer to our article on RAM speed.
When You Run Out of RAM
All modern operating systems have something called a page file, also known as a swap file, which is a special file on your data drive that temporarily stores data from RAM. It comes into play when your computer needs to juggle too much data that can't fit entirely on the RAM modules alone.
To make up for this lack in RAM capacity, the least-used data is outsourced to the page file and becomes what's known as virtual memory.
As such, over time, the page file can grow in size and exceed hundreds of MBs, though the operating system can set limits to the size of your page file, usually giving you as much virtual RAM as the amount of physical RAM on your system.
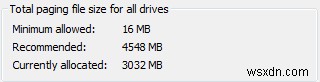
Should you ever see an error message indicating that you're running low on virtual memory, it means that you're nearing the size limit of your page file.
On Windows, you can manually increase the size of the page file via the Control Panel, which we have covered in our article on How to Fix Low Memory.
Note that when the system has to access data stored in the page file, it can slow down your computer because data drives are much slower than RAM modules. Thus, rather than increasing your page file, you should consider installing more RAM.
RAM Data Can Be Compressed
In Windows 10, the page file still exists, but before the system outsources data to your local drive, Windows 10 compresses least-used RAM data. Compression can reduce the size of stored data by up to 60%.
Microsoft estimates that as a result of memory compression, the Windows 10 page file is used half as much as in previous Windows versions. You can see it in action in your Task Manager as System and compressed memory.
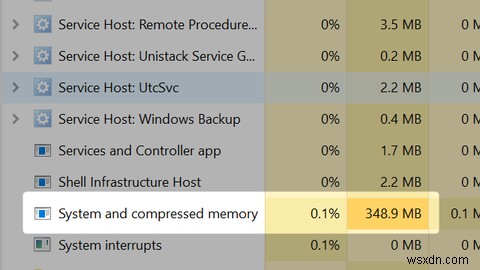
Note that memory compression isn't a novel feature. It's been known as ZRAM in Linux or ZSWAP on Android long before Windows 10 became available.
The only potential downside of memory compression is that the tool that handles the compression -- the Memory Manager -- demands extra processing power. If it isn't managed well, RAM compression can lead to high CPU usage of the System and compressed memory item seen in the Task Manager.
This common Windows 10 issue is typically fixed by disabling hibernation, updating the BIOS, or -- when you also observe a high CPU load for System Interrupts -- updating memory- and storage-related drivers with Windows 10-compatible versions.
Smart RAM Management With SuperFetch
SuperFetch is a Windows tool that improves memory management in several different ways.
First, SuperFetch analyzes how you use your computer and notes patterns, such as the usual times at which certain files and programs are accessed. Second, SuperFetch collaborates with the Windows defragmenter to store files in the order that they are typically accessed. Finally, it can pre-load applications into memory at opportune times.
Overall, SuperFetch contributes to the efficient use of available memory to speed up Windows boot time and make applications launch faster.
It's possible to disable SuperFetch if it negatively impacts disk performance, but in the absence of this issue, we strongly suggest you keep SuperFetch enabled! While turning SuperFetch off might increase the amount of available memory, it will have a negative impact on your system's performance.
ReadyBoost: Only for Hard Disk Drives
ReadyBoost is a neglected Windows feature that works similar to SuperFetch. It analyses user activity and writes information to designated flash drives or SD cards. This type of cache is faster than information stored on a notoriously slow hard drive and can thus improve computer performance.
With the rise of solid state drives, however, ReadyBoost has lost much of its advantages. But if you're still using a hard disk drive and are curious about ReadyBoost, we have covered it in our piece on how to increase RAM, although strictly speaking ReadyBoost doesn't actually increase available RAM.
RAM Reloaded
With all the tools designed to optimize memory management, your RAM shouldn't need a lot of babysitting. Just make sure you install the right amount and version of RAM and you should never run out of memory. In the worst case, increase the size of your page file or try out ReadyBoost.
If you use a Mac, have a look at how to check your Mac's memory for problems.
Have you come across any other RAM-related terms we should know? Or can you recommend any tools to manage memory? Please share with us in the comments!
